Earth Applied Sciences Program led the development of a new special issue of the journal Remote Sensing of Environment (Impact Factor=8.2). Titled Earth Observations for Sustainable Development Goals (SDG), it showcases the application of Earth observation data and the role they play in driving and tracking progress on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) as set by the United Nations to achieve a better and more sustainable future for all.
The special issue includes seventeen publications highlighting Earth science contributions to support countries in target setting, tracking progress on the SDG, and informing sustainable development planning and decision making. Earth Applied Sciences worked on the journal special issue with the University of New South Wales and the Australian federal government research agency, the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (CSIRO).
The special issue adds evidence in that most of the SDG indicators for which Earth observations provide significant contributions require additional information for their accurate estimation, including census data, field collection data and information from spatial databases on soil, climate, land ownership etc. (Vaz et al., 2019; Prince, 2019; Mulligan et al., 2020).
In some cases, Earth observations only contribute indirectly to SDG indicators (Stokes and Seto, 2019; Mulligan et al., 2020; Mason et al., 2020) but still provide a relevant data and information dimension.
There are 17 SDGs. The most direct connections between SDG indicators and Earth observation systems are within Goal 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation) and 15 (Life on Land), followed by 14 (Life below Water) and 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities), and that is indirectly confirmed by the dominance of papers of this special issue focused on those goals.
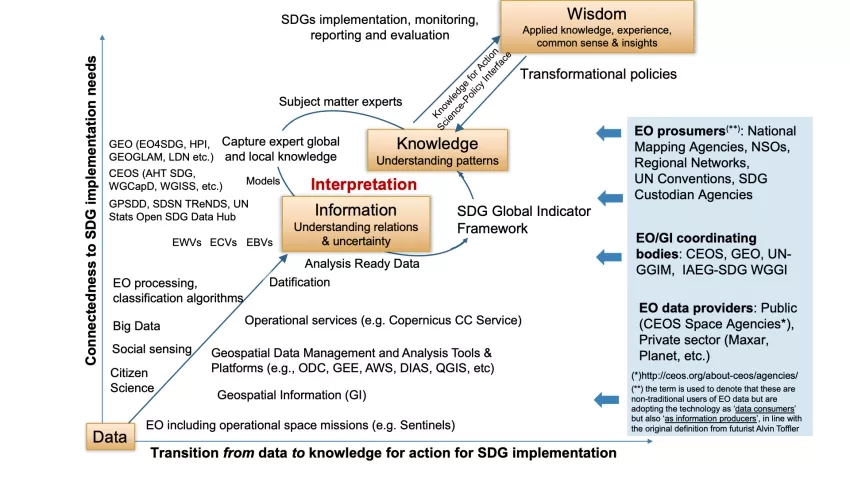
Our review illustrates that an urgent need exists for transitioning towards new Earth observation for SDG frameworks that are focused on the knowledge element of the data-information-knowledge-wisdom paradigm, rather than the data and information aspects.
The special issue includes an editorial titled, "Towards delivering on the sustainable development goals using earth observations" which summarizes the content and includes more information about the 17 contributions and how Earth observation data, methods, and tools can, and already, support countries in target setting for the SDG, including baseline determination, as well as tracking of progress on SDG implementation and informing sustainable development planning and decision making.