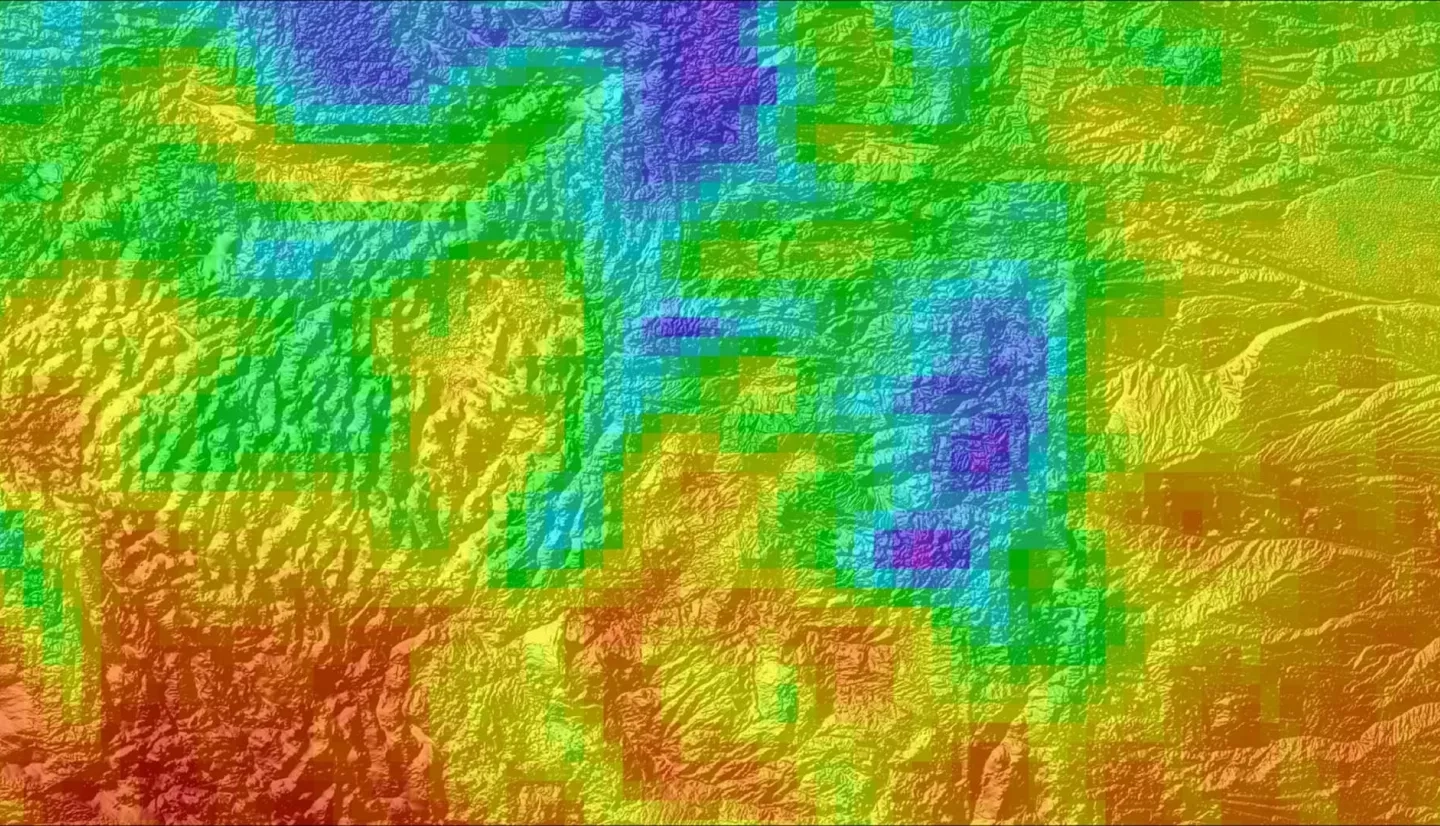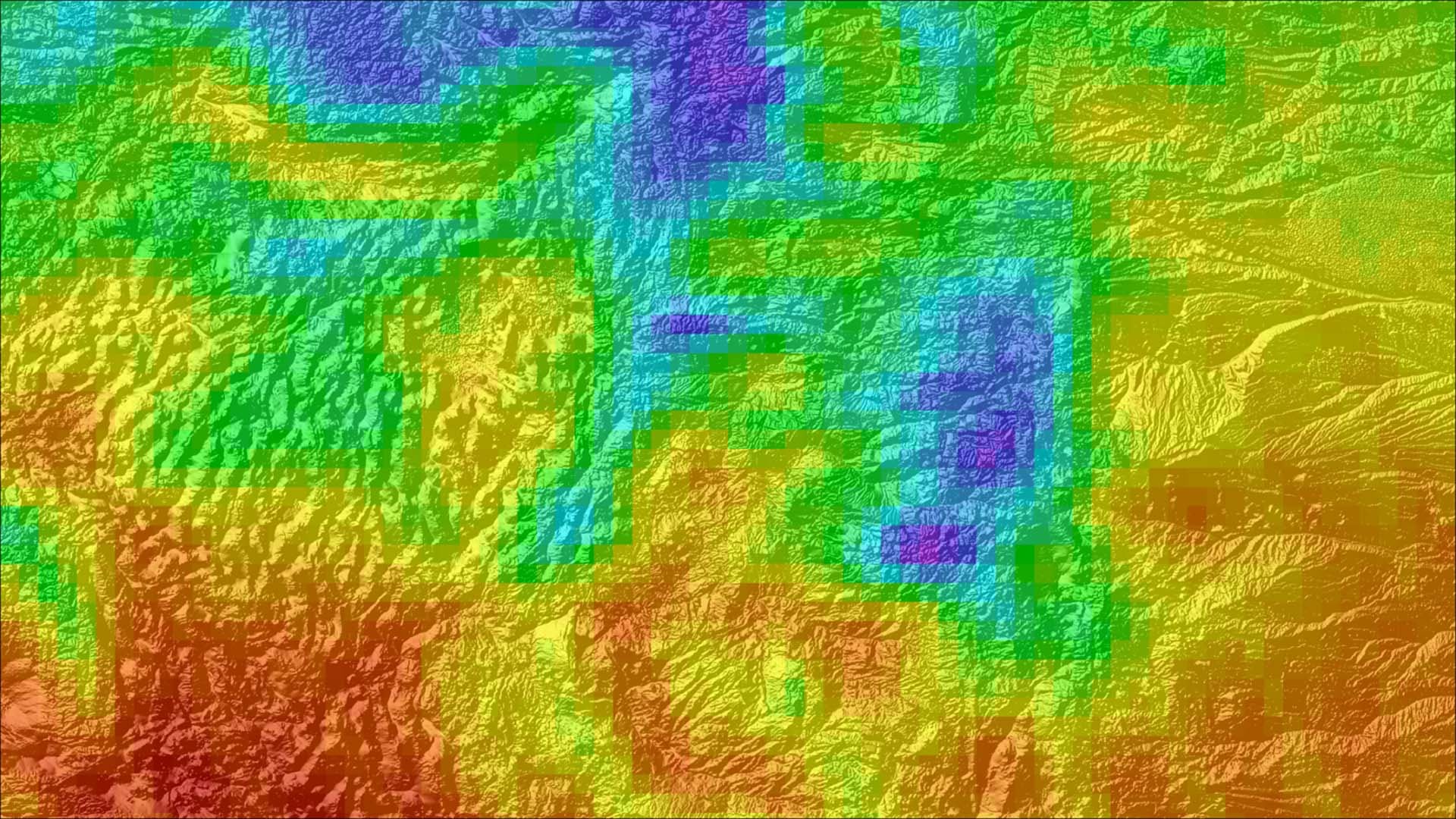
Good air quality is critical for the Intermountain Region of the National Park Service (NPS) to uphold legal mandates, such as the Clean Air Act, to protect park visitor health, the ecological health of the park flora and fauna, and the preservation of the vistas of the parks for the present and future generations. Unfortunately, nitrogen dioxide (NO2) harms air quality related values and the health of guests that visit the parks. This project utilized the Ozone Monitoring Instrument aboard Aura, a NASA Earth observation satellite, to create spatial and temporal trend maps as well as visual displays of NO2 data from January 2005 to December 2017. By applying NASA Earth observations, the NPS can complement their ground-level data from monitoring programs. This uncovers trends of persistent concentrations of NO2 in the Intermountain Region and its surrounding areas. With the help of NASA Earth observations, the NPS is able to determine source regions of NO2, allowing them to develop mitigation strategies and create long term management action plans involving visibility, air quality, and the parks' natural resources.