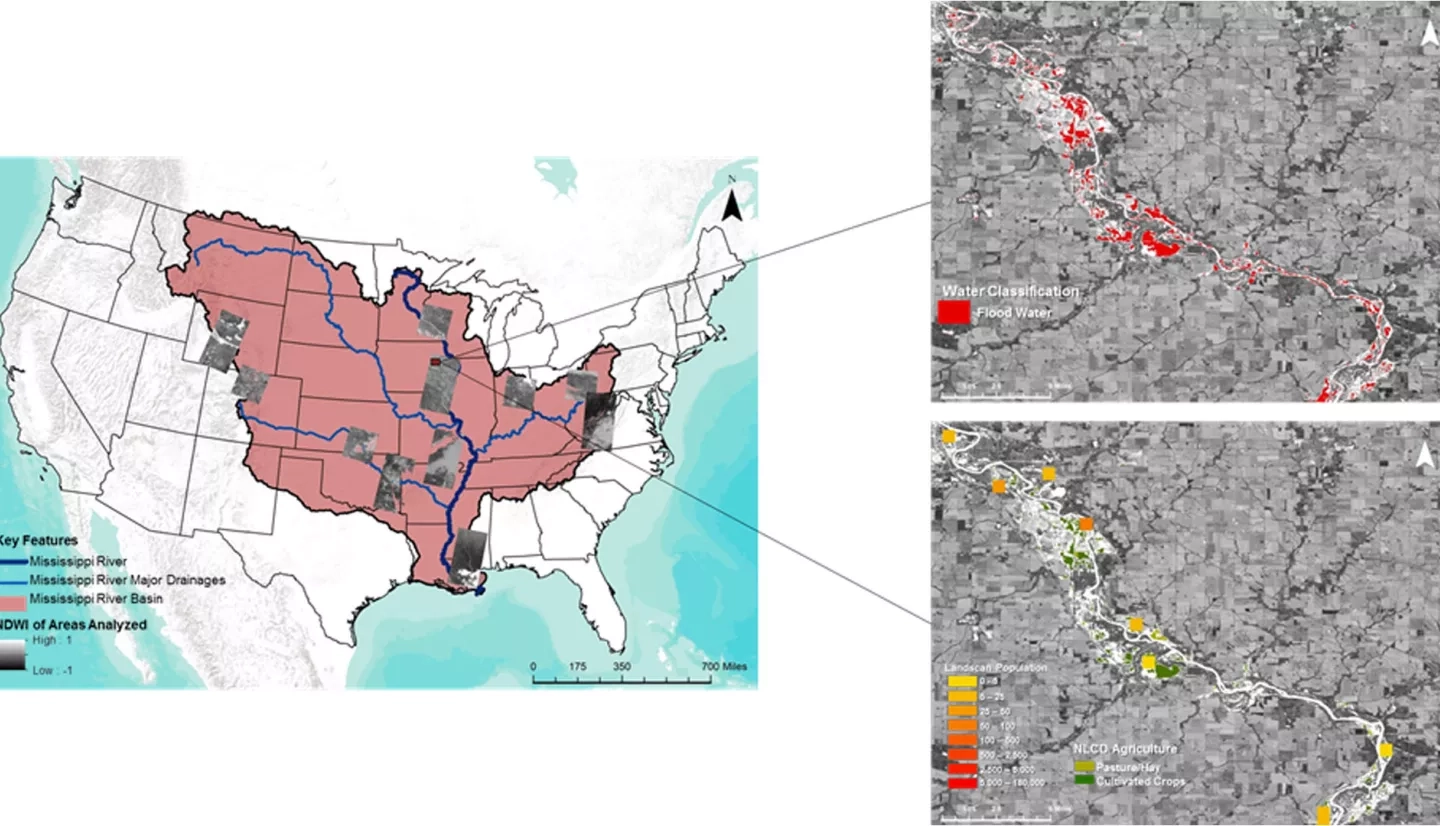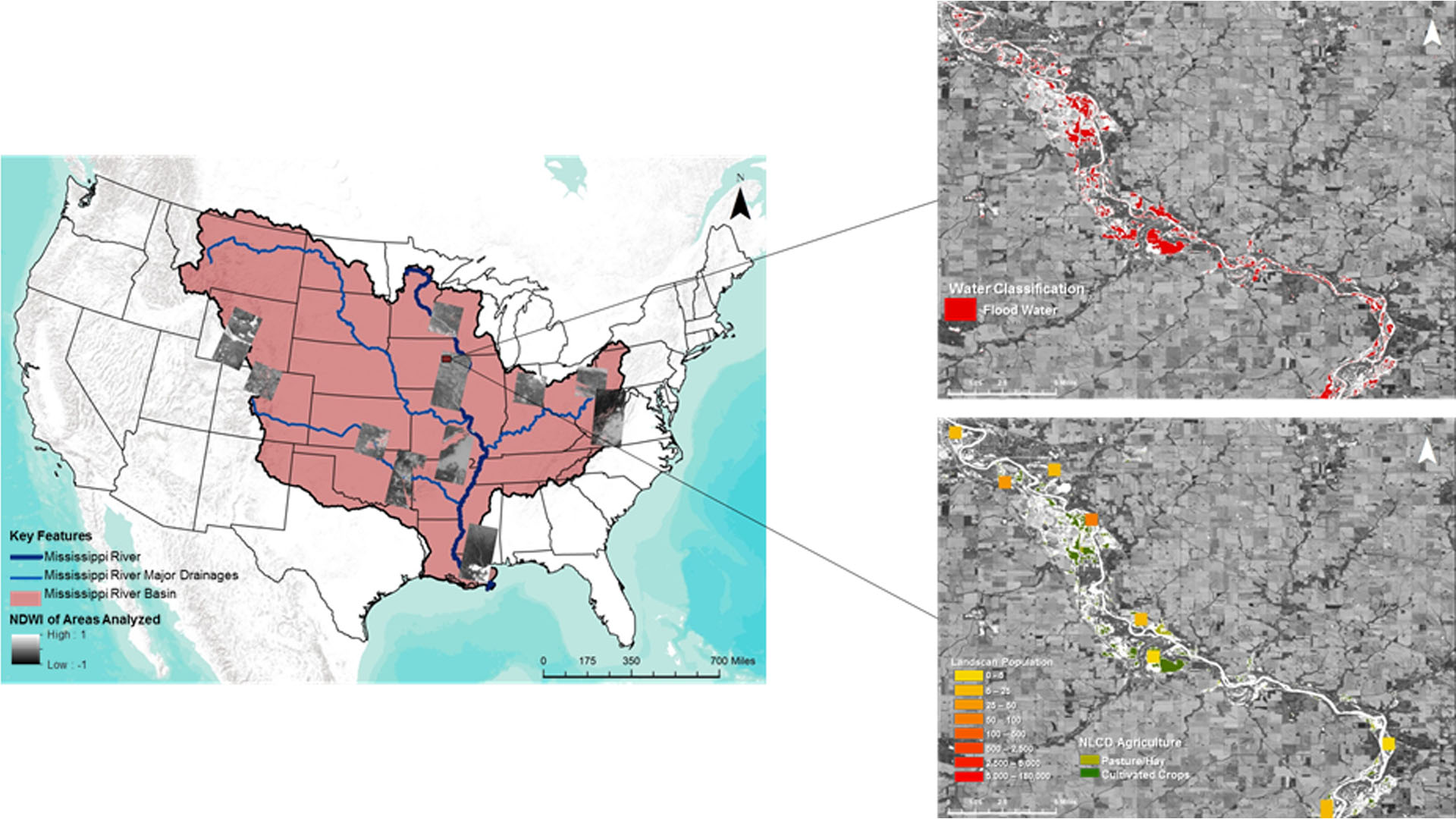
The Mississippi River Basin is the fourth largest drainage basin in the world, and is susceptible to multi-level flood events caused by heavy precipitation, snow melt, and changes in water table levels. Conducting flood analysis during periods of disaster is a challenging endeavor for NASA's Short-term Prediction Research and Transition Center (SPoRT), Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), and the US Geological Survey's Hazards Data Distribution Center (USGS HDDS), due to heavily-involved research and lack of manpower. During this project, an automated script was generated that performs high-level flood analysis to relieve work load for end-users. The script incorporated Landsat 8 Operational Land Imager (OLI) tiles and utilized computer-learning techniques to generate accurate water extent maps. The script referenced the Terra Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) land-water mask, to isolate areas of flood induced waters. These areas were overlaid onto the National Land Cover Database's (NLCD) land cover data, the Oak Ridge National Laboratory's LandScan data, and Homeland Infrastructure Foundation-Level Data (HIFLD) to determine the classification of areas impacted and the population density affected by flooding. The automated algorithm was tested on multiple flood events within the Mississippi River Basin, and focused on the September 2016 flood event that occurred in Upper Mississippi River Basin. This script allows end-users to create their own flood probability and impact maps for disaster mitigation and recovery efforts.