- PI: Tony Chang, Vibrant Planet, PBC
- Co-I: Bogdan State, Vibrant Planet, PBC
- Co-I: Leo Tsourides, Vibrant Planet, PBC
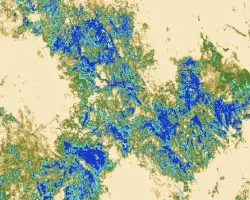
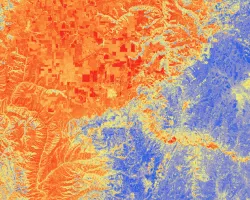
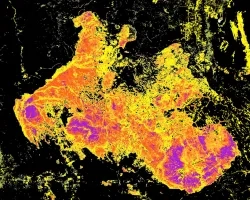
Climate change is expected to alter wildfire potential at a global scale with increased fire frequency and lengthened seasons. This change in wildfire potential has generated urgency for information on local/regional scale wildfire risk and behavior in order to aid forest managers in mitigating human loss of life, property damage, and ecosystem service degradation. One critical aspect in monitoring wildfire potential is accurate and high resolution spatial forest structure data. This project focuses on developing a Deep Learning model that estimates a fine-grained canopy height model (CHM) that is trained and calibrated from National Agricultural Imagery Program (NAIP) images, USGS 3DEP lidar data, and the GEDI global lidar product.
The output of this project will allow for an improved understanding of regional forest structure that is vital for multi-objective forest management planning (e.g. community safety, watershed health, biodiversity enhancement, catastrophic fire mitigation, etc.) within multi-jurisdictional ownership. These national-scale modeled forest metrics will be directly ingested into USFS wildfire modeling software to understand wildfire risk and behavior in a wall-to-wall spatial manner at a bi-annual temporal interval to allow for ‘near-real’ time fire risk assessment and more proactive fuels management decisions.