Description
Remote sensing data is becoming crucial to solve some of the most important environmental problems, especially pertaining to agricultural applications and food security. Effectively working with this large data source requires different tools and processing, such as cloud computing and infrastructure. Participants will become familiar with data format and quality considerations, tools, and techniques to process remote sensing imagery at large scale from publicly available satellite sources, using cloud tools such as AWS S3, Databricks, and Parquet. Additionally, participants will learn how to analyze and train machine learning models for classification using this large source of data to solve environmental problems with a focus on agriculture. Participants will have a basic understanding of tools such as Pyspark and TensorFlow. We hope that participants in this course will walk away with the skills and tools to train algorithms using satellite imagery to solve environmental problems anywhere on the planet.
OPTIONAL: To follow along with the demonstrations for this training, please create an account to login to Databricks prior to the training start date.
By the end of this training attendees will be able to:
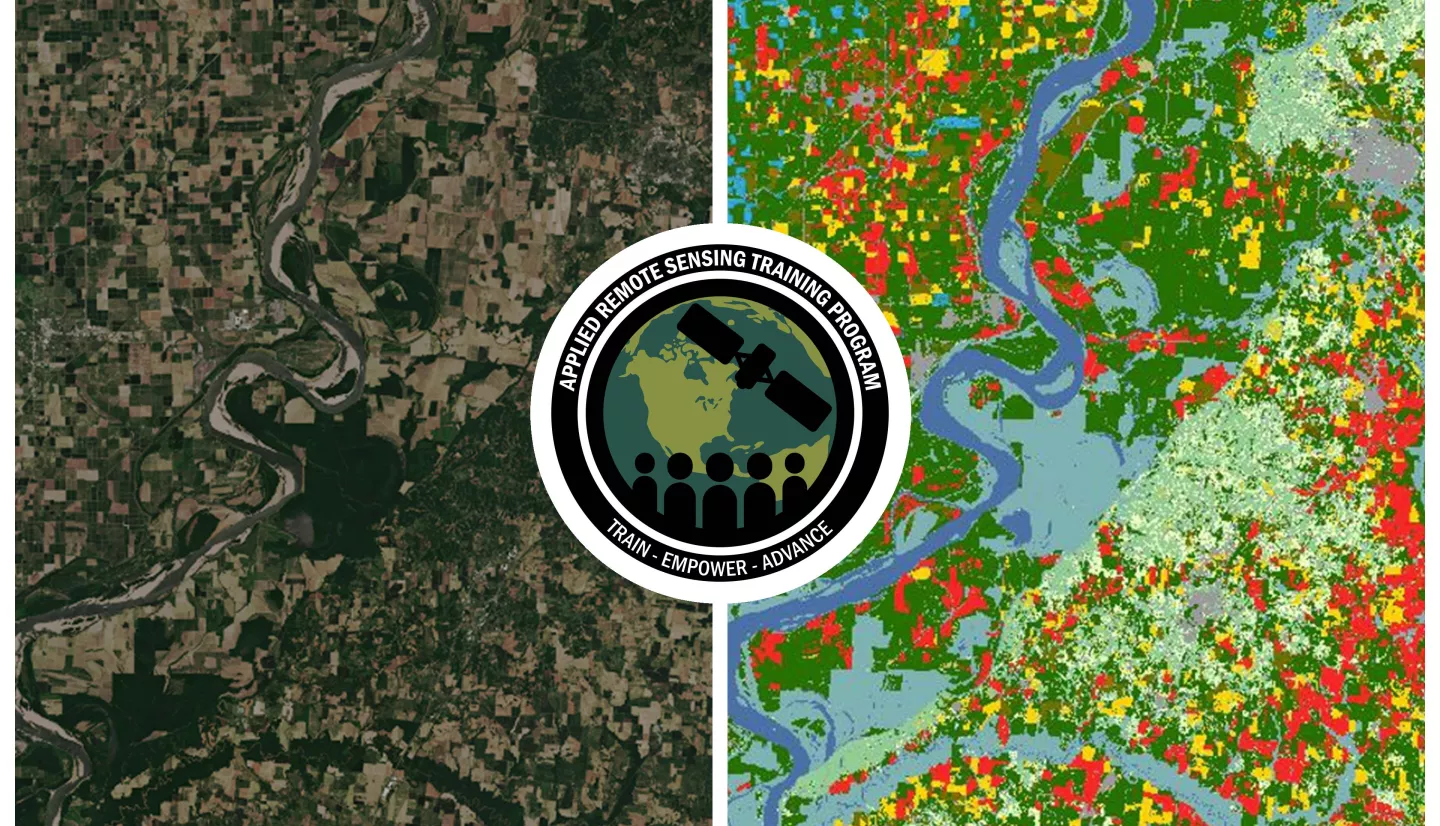
- Use recommended techniques to download and process remote sensing data from Sentinel-2 and the cropland data layer (CDL) at large scale (> 5GB) with cloud tools (Amazon Web Services [AWS] Simple Storage Service [S3], Databricks, Spark, Parquet)
- Filter data from both the measured (satellite images) and target (CDL) domains to serve modeling objectives based on quality factors, land classification, area of interest [AOI] overlap, and geographical location.
- Build training pipelines in TensorFlow to train machine learning algorithms on large scale remote sensing/geospatial datasets for agricultural monitoring
- Utilize random sampling techniques to build robustness into a predictive algorithm while avoiding information leakage across training/validation/testing splits
Primary Target Audience: Remote sensing scientists, practitioners, and geospatial analysts from local, regional, federal, and non-governmental organizations who use remote sensing for agricultural applications.
Secondary Target Audience: Agronomists, data scientists/data engineers/ML engineers.
Other Potential Participants: Any practitioners of remote sensing data.
Three parts, 1.5 hour each, held twice daily (2 sessions per part).
Trainers: Sean McCartney
Guest Instructors: John Just (Deere & Co.), Erik Sorensen (Deere & Co.)
- Submit lists of boundaries to the NASS API and retrieve CDL rasters back
- Subsample and visualize retrieved data from CDL with interactive spatial images and other statistical plots
- Obtain Sentinel-2 raster files for a given area and timeframe corresponding to the retrieved CDL data and manipulate the sentinel-2 rasters into tables in preparation for analysis and model training.
- Verify correct processing of data via various interactive plots (e.g. time series of pixels of various land covers).
Materials
Following each weekly Part there will be an OPTIONAL self-paced learning exercise, which will not be graded, but serve as a knowledge check and prepare you for the following parts of the webinar series, as well as the final homework assignment. There will be one homework assignment which will be posted on March 19th.
- Databricks Setup Instructions: To be completed before starting individual learning exercises and the homework assignment.
- Optional Part 1 Learning Exercise
Materiales en Español:
Trainers: Sean McCartney
Guest Instructors: John Just (Deere & Co.), Erik Sorensen (Deere & Co.)
- Follow the process to set up a Tensorflow data loader that works with Parquet files to create a training pipeline suitable for training a model on large-scale data
- Perform steps to manipulate the imagery data stored in tables, normalize the values, and bucketize irregularly spaced time-series data to prep for modeling
- Follow steps to parallelize/prefetch preprocessing for fast training
- Apply the correct procedure to split time-series data into train/val/test sets to avoid data leakage
Materials
Following each weekly Part there will be an OPTIONAL self-paced learning exercise, which will not be graded, but serve as a knowledge check and prepare you for the following parts of the webinar series, as well as the final homework assignment. There will be one homework assignment which will be posted on March 19th.
- Databricks Setup Instructions: To be completed before starting individual learning exercises and the homework assignment.
- Optional Part 2 Learning Exercise
Materiales en Español:
Trainers: Sean McCartney
Guest Instructors: John Just (Deere & Co.), Erik Sorensen (Deere & Co.)
- Perform the process to set up and train a 1-D convolutional neural network (CNN) model that learns to detect crop-type from a satellite image
- Follow steps to monitor model performance during training and how to choose appropriate hyperparameter adjustments
- Plot predictions to validate performance after training
Materials
Following each weekly Part there will be an OPTIONAL self-paced learning exercise, which will not be graded, but serve as a knowledge check and prepare you for the following parts of the webinar series, as well as the final homework assignment. There will be one homework assignment which will be posted on March 19th.
- Databricks Setup Instructions: To be completed before starting individual learning exercises and the homework assignment.
- Optional Part 3 Learning Exercise
- Homework Assignment (Due April 01, 2024)
Materiales en Español:
- Fundamentals of Remote Sensing
- Agricultural Crop Classification with Synthetic Aperture Radar and Optical Remote Sensing Parts 1 & 2 only
- Mapping Crops and their Biophysical Characteristics with Polarimetric SAR and Optical Remote Sensing Parts 1 & 2 only
- Crop Mapping using Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and Optical Remote Sensing Part 2 only